Karl Bodmer
by Jean François Millet (1814–1875)
Courtesy the Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Division of Art, Prints and Photographs: Print Collection, The New York Public Library.[1]“Portrait of Karl Bodmer” New York Public Library Digital Collections. Accessed16 January 2023. digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/a38d0950-aab9-0139-152b-0242ac110002.
Swiss artist Karl Bodmer, was employed by Prince Maximillian von Wied (1809-1893) to accompany him on a journey to the upper Missouri River. By virtue of the timing of the 1832 trip, his drawings—and the paintings and engravings derived from them—have also become associated with the Lewis and Clark Expedition.
Pages with Bodmer’s Artwork
November 27, 1804
Mandan deceptions


Lewis returns to Fort Mandan with two Hidatsa chiefs, and the captains learn that the Mandans have been telling lies to the Hidatsas. Seven Canada-based traders arrive at the Knife River Villages.
January 23, 1805
Making sleds


At Fort Mandan below the Knife River Villages, the enlisted men awake to four inches of fresh snow and go about their ‘common’ day. Sleds are made and traded for locally grown beans and corn.
The White Cliffs
by Joseph A. Mussulman

Under cloudy skies on the morning of 31 May 1805, the expedition “proceeded at an early hour,” and roped their flotilla of six cottonwood dugout canoes and two big pirogues into one of the most famous riverscapes on the Missouri.
August 10, 1804
Blackbird Hill in view


The boats sail 22½ miles up the Missouri River, and they encamp within view of Blackbird Hill. Lewis collects the earliest plant specimen that survives today, field horsetail.
September 24, 1804
Buffalo Medicine


At present Pierre, South Dakota, the captains smoke with Buffalo Medicine, and a promise is made to return Pvt. Colter’s stolen horse and to meet with the captains tomorrow.
March 11, 1805
Charbonneau's corruption


At Fort Mandan below the Knife River Villages, the captains accuse Hidatsa interpreter Toussaint Charbonneau of acting in the interests of local fur traders and give him an ultimatum.
Fur Trade after the Expedition
by W. Raymond Wood

The Louisiana Purchase and the lure of its beaver population led to a veritable flood of traders and trappers moving toward the Upper Missouri and the Northern Rocky Mountains and the slow abandonment of the overland trade in the United States by Canadian and British interests.
February 16, 1805
Scorched earth


Many miles south of Fort Mandan and the Knife River Villages, Lewis and his soldiers continue their pursuit of a Sioux war party. They come to an old Mandan village where two lodges have been set afire.


Meriwether Lewis listed a “Keeled Boat” in his pre-expedition shopping list, but after he finally got it, he and the other journalists of the Corps of Discovery simply called it “the boat” (190 times) or, less often, “the barge” (32 times).


The two captains and ten of the enlisted men climbed the hill to visit the grave of one of the most notorious and controversial leaders of the Omaha Nation, whose name was Washinga Sahba—Blackbird.
April 20, 1805
An Assiniboine grave


Below present Williston, North Dakota, hard winds prevent the boats from making more than seven miles up the Missouri. Lewis walks on shore and observes a partially fallen Assiniboine scaffold grave.
January 25, 1805
Assiniboine traders


At Fort Mandan, the enlisted men continue making charcoal for the blacksmiths and trying to free the boats from the Missouri River ice. At the Knife River Villages, a band of Assiniboine traders arrives.
January 11, 1805
War medicine dance


Posecopsahe (Black Cat) of Ruptáre and The Coal of Mitutanka visit Fort Mandan and spend the night. At Mitutanka village, several soldiers witness a war medicine dance—perhaps the Mandan Wolf Ceremony.
March 17, 1804
War tactics


The enlisted men at Wood River, Illinois enjoy spring-like weather while the captains are away. During this time, Clark finalizes questions about the war tactics of the Native Nations they will soon meet.
January 16, 1805
Hidatsa-Mandan jealousy


At Fort Mandan, the captains attempt to smooth over Hidatsa and Mandan jealousy. Lewis demonstrates the air gun and cannon, and the captains caution Seeing Snake not to war with the Shoshones.
April 14, 1805
Bear Den Creek


Bear Den Creek, ND Passing sage-covered hills, the expedition makes fourteen miles up the Missouri River. They notice prairie dogs, elk, buffalo and two empty Assiniboine camps.
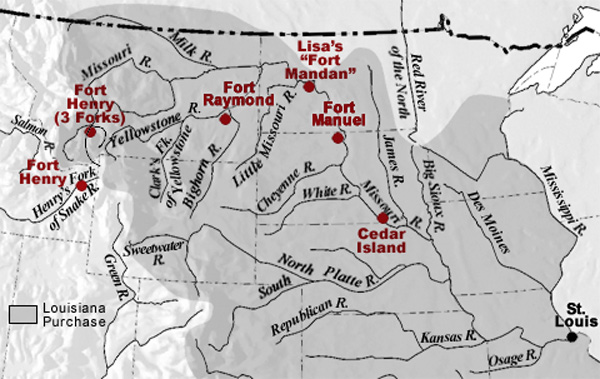

Manuel Lisa’s men at Fort Raymond not only encouraged the Crows to come trade with them, but they set out parties to trap beaver on their own. It was the latter effort that led to hostilities with the Blackfeet that affected Potts, Drouillard, and Colter.
January 13, 1805
Major buffalo hunt
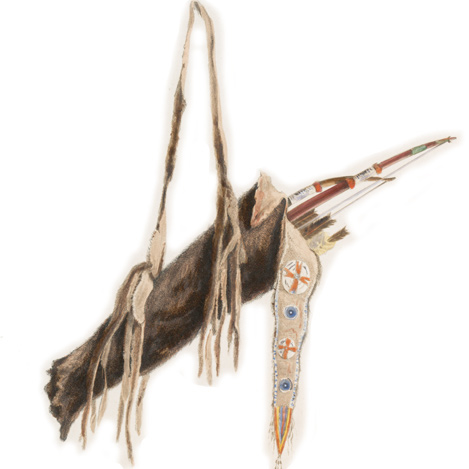


At Fort Mandan, Clark estimates that half the Mandan population has formed a large hunting party. Charbonneau returns from a trip and tells Clark why Hidatsa Chief Le Borgne has kept his distance.
October 12, 1804
Trading with the Arikara


At an Arikara village, the morning is spent parleying and trading. At 1 pm, the expedition heads up the Missouri River and encamps near present Shaw Creek Recreation Area in South Dakota.
April 22, 1804
Our Missouria Indian


The captains are working in St. Louis with Pierre Chouteau‘s Osage delegation. An undated note says the captains have decided not to bring along a Missouria Indian that has been with them this past winter.


Several vexillologists have speculated that Lewis and Clark might have carried some “Indian presentation flags” with seventeen stripes, plus the Great Seal in the canton with seventeen stars either surrounding the eagle or inside the Glory.
John Robinson
(ca. 1780–unknown), Corporal
This man is perhaps the most mysterious of the expedition’s mystery men. Journal entries indicate he may have left the expedition on 12 June 1804 riding back to St. Louis with Chouteau Fur Company traders.


Lewis and Clark first met the Teton Sioux on 25 September 1804. One of Jefferson’s primary political objectives for the expedition was to create a peace treaty and trade agreement them, the most potent military and economic force on the lower Missouri.
August 31, 1804
Yankton speeches


The council with the Yankton Sioux continues with many of them giving speeches while Clark and Sgt. Ordway take notes. Trader Pierre Dorion is assigned a mission to make peace with the region’s Nations.
August 19, 1806
Jusseaume's leather lodge


Due to high winds, they make only ten miles down the Missouri. At evening camp near present Huff, North Dakota, interpreter René Jusseaume offers Clark space in his leather lodge.
May 5, 1805
Wolves and grizzlies


As the boats move 17 miles up the Missouri, they stop to repair the white pirogue’s rudder. Clark tells of difficulty with a “turrible looking” grizzly bear. Camp is near present Wolf Point, Montana.
January 20, 1805
Mandan gratitude ritual


Sgt. Gass witnesses some Mandans offering food to a sacred buffalo skull, and Clark explains yesterday’s jealousy between the two interpreters’ wives. The gunsmithing skills of Pvt. Shields is described..
April 2, 1804
Northward-bound traders


At winter camp across from the mouth of the Missouri, Clark says the men are “a cleaning to Day.” A boat bound for Prairie du Chien and owned by Mississippi River trader Nicholas Jarrot stops for the night.


After Lewis’s preliminary sketch, later artists and photographers contributed to the visual documentation of the “sublimely grand” waterfall including Barralet, Gustavus Sohon, A. E. Mathews, and F. Jay Haynes.
August 14, 1806
Among old friends


The expedition arrives at the Knife River Villages—one of which is the home of the Charbonneau family. The captains meet with various chiefs, and Clark invites them to travel to Washington City.


In 1673 French explorers Père Marquette and Louis Joliet listened to local Indians’ warnings about this place and erected a cross atop the ninety-foot-high rock to disempower the demons said to be lurking in the treacherous whirlpool at its base.
November 30, 1804
A military reprisal


Responding to news of a deadly Sioux and Arikara attack on Mandan hunters about 25 miles from Fort Mandan, Clark leads a military force to Mitutanka to gather warriors and pursue the attackers.
August 15, 1806
Broken promises of peace


At the Knife River Villages in present North Dakota, the captains hear of several broken promises of peace among the tribes with whom they had established peace agreements on the outward journey.
Assessing the Legacy of Lewis and Clark
by Clay S. Jenkinson

The author proposes a few metaphors for the Lewis and Clark story, not in any definitive way, but merely to help us all think about the legacy of the expedition.
August 30, 1804
Yankton council and dance


At a council with the Yankton Sioux, Lewis delivers a speech, gifts given, and a peace pipe passed. Clark learns about the Akicita Society, and Sgt. Ordway finds their musical instruments interesting.
June 6, 1806
Still no guides


Clark travels to Broken Arm’s village to repeat a diplomatic speech and ask for guides. He is given two peace pipes—one for him and the other for the Shoshones. Lewis describes the western tanager.


One of the animals recorded by Lewis and Clark—and which became one of the staples of their mostly carnivorous diet—was the wapiti, or American elk (Cervus elaphus).


Next to grizzly bears and Mother Nature, the most feared enemy of American fur trappers traveling along the upper Missouri River were the Niitsítapi or Blackfeet, the “Original People” or “Prairie People.” Was that Lewis’s fault?
March 13, 1804
Native traditions


Clark and Lewis are likely working in St. Louis while the enlisted men continue at Wood River, Illinois under the charge of Sgt. Ordway. Perhaps Clark works on the questions about Indian traditions and history.
Notes
| ↑1 | “Portrait of Karl Bodmer” New York Public Library Digital Collections. Accessed16 January 2023. digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/a38d0950-aab9-0139-152b-0242ac110002. |
|---|
Experience the Lewis and Clark Trail
The Lewis and Clark Trail Experience—our sister site at lewisandclark.travel—connects the world to people and places on the Lewis and Clark Trail.
Discover More
- The Lewis and Clark Expedition: Day by Day by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 2018). The story in prose, 14 May 1804–23 September 1806.
- The Lewis and Clark Journals: An American Epic of Discovery (abridged) by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 2003). Selected journal excerpts, 14 May 1804–23 September 1806.
- The Lewis and Clark Journals. by Gary E. Moulton (University of Nebraska Press, 1983–2001). The complete story in 13 volumes.


